AI : A Comprehensive Exploration of Artificial Intelligence in 2024
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as one of the most transformative technologies of our time, revolutionizing industries, augmenting human capabilities, and reshaping our understanding of what machines can accomplish. From intelligent virtual assistants and recommendation systems to autonomous vehicles and medical diagnostics, it is permeating every aspect of modern life.
In this extensive blog, we will embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of it, exploring its history, core concepts, applications across various domains, ethical considerations, and the future trajectory of this groundbreaking field. Whether you’re a novice curious about it’s potential or a seasoned professional seeking deeper insights, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence.
Contents :
What is AI ?
it refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and problem-solve like humans. The goal of it is to develop systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from experience.
encompasses a broad range of techniques and approaches, including:
- Machine Learning: Machine learning is a subset of that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to process data and extract meaningful patterns or features. It has been particularly successful in tasks such as image and speech recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a branch of it that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It is used in applications such as chatbots, language translation, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision involves enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from the real world, such as images and videos. It is used in applications like facial recognition, object detection, and autonomous vehicles.
- Robotics: Robotics combines with engineering to design and develop machines (robots) that can perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. Robots equipped with it can navigate environments, manipulate objects, and interact with humans.
it has a wide range of applications across various industries and sectors, including healthcare, finance, transportation, manufacturing, entertainment, and more. Some common examples of it applications include virtual assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), recommendation systems (e.g., Netflix, Amazon), autonomous vehicles, medical diagnosis systems, and predictive analytics.
As technology continues to advance, researchers and developers are exploring new techniques, algorithms, and applications to further enhance its capabilities and address complex challenges facing society. However, along with its potential benefits, it also raises ethical, societal, and economic considerations, such as bias in algorithms, job displacement, privacy concerns, and the impact on labor markets. Therefore, responsible development and deployment are essential to ensure that it benefits humanity while mitigating potential risks.
Current Status :
As of the current status, it is experiencing a period of unprecedented growth, innovation, and adoption across various sectors. Here’s an overview of the current state:
- Advancements in Deep Learning: Deep learning, a subset of machine learning inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, has propelled to new heights. Neural networks with multiple layers are capable of learning intricate patterns from vast amounts of data, leading to breakthroughs in computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
- Applications Across Industries: it is being deployed in diverse industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, retail, manufacturing, and entertainment. In healthcare, it is revolutionizing medical imaging, drug discovery, patient monitoring, and personalized treatment. In finance, powered algorithms are used for fraud detection, risk assessment, trading, and customer service. Similarly, it is enhancing customer experiences, optimizing supply chains, and improving operational efficiency in other sectors.
- Autonomous Systems: Autonomous vehicles represent a prominent application of it, with companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber investing heavily in self-driving technology. Beyond transportation, it is driving advancements in autonomous drones, robots, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for applications such as surveillance, delivery, and exploration.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Conversational : NLP technologies enable machines to understand, generate, and interact with human language. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and chatbots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, providing users with personalized recommendations, assistance, and information retrieval.
- Ethical and Societal Considerations: The ethical implications of it, including bias, fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy, are receiving greater scrutiny as systems become more pervasive. Efforts to develop ethical guidelines, standards, and regulatory frameworks are underway globally to ensure responsible development and deployment.
- Research and Collaboration: it research is a collaborative endeavor involving academia, industry, and government organizations worldwide. Major tech companies, such as Google, Microsoft, Facebook, and OpenAI, are investing in research and development, contributing to the advancement of the field through open-source initiatives, academic partnerships, and conferences.
- The Future of Work: The integration of technologies into the workforce is reshaping job roles, skill requirements, and employment patterns. While it has the potential to automate routine tasks, it also creates opportunities for human collaboration, upskilling, and the creation of new jobs in development, data science, and ethics.
- Challenges and Opportunities: Despite its tremendous potential, it faces challenges such as data biases, algorithmic fairness, cybersecurity threats, and the ethical implications of driven decision-making. Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary collaboration, ongoing research, and responsible governance to ensure that benefits society as a whole.
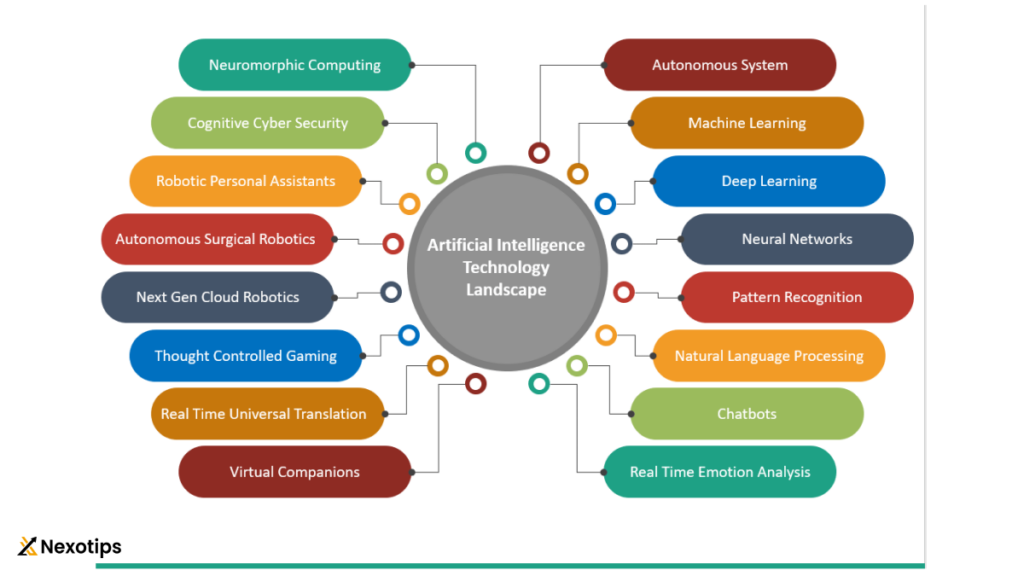
challenges of AI:
As of the present day, several challenges persist in the field of it hindering its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. Here are some of the current challenges:
- Data Quality and Availability: it’s algorithms rely heavily on high-quality, labeled data for training. However, obtaining large, diverse, and clean datasets can be challenging, particularly in domains where data is scarce, biased, or proprietary. Ensuring data quality, diversity, and accessibility remains a significant hurdle.
- Ethical and Bias Concerns: systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Addressing ethical concerns surrounding bias, fairness, transparency, and accountability in decision-making is crucial for fostering trust and preventing harm to individuals and communities.
- Interpretability and Explainability: models, particularly deep neural networks, are often viewed as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their predictions or decisions. Enhancing the interpretability and explainability of systems is essential for ensuring transparency, trustworthiness, and regulatory compliance.
- Robustness and Security: systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate input data to deceive the model’s predictions. Ensuring the robustness and security of it systems against adversarial threats, data poisoning, and model stealing is critical for safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities and ensuring system reliability.
- Scalability and Efficiency: it models, particularly deep learning architectures, require significant computational resources and energy consumption during training and inference. Developing scalable, energy-efficient algorithms and hardware solutions is essential for reducing costs, environmental impact, and enabling deployment in resource-constrained environments.
- Regulatory and Legal Frameworks: The regulatory landscape for it is still evolving, with limited consistency and harmonization across jurisdictions. Establishing clear guidelines, standards, and regulations for development, deployment, and governance is essential for ensuring ethical and responsible practices, protecting user rights, and mitigating potential risks.
Future of AI:
it holds immense promise and potential to transform virtually every aspect of human society. Here are some key trends and possibilities that may shape the future:
- Powered Healthcare: technologies are poised to revolutionize healthcare by enabling more accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and efficient healthcare delivery. driven medical imaging, predictive analytics, drug discovery, and remote patient monitoring have the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance healthcare accessibility.
- Autonomous Systems: Autonomous vehicles represent a prominent application of it, with the potential to revolutionize transportation, logistics, and urban mobility. Beyond self-driving cars, powered drones, robots, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are expected to play critical roles in areas such as agriculture, infrastructure inspection, disaster response, and space exploration.
- Conversational and Virtual Assistants: Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies are advancing rapidly, enabling more sophisticated conversational systems and virtual assistants. Future developments may include it’s companions, virtual tutors, and personalized assistants capable of understanding and responding to human emotions, context, and preferences.
- Personalization and Recommendation: algorithms are increasingly used to personalize user experiences and provide tailored recommendations in areas such as e-commerce, entertainment, social media, and content delivery. Future advancements may involve systems that anticipate user needs, preferences, and behaviors more accurately, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
- Augmented Creativity: technologies are increasingly being used as creative tools to assist artists, designers, writers, and musicians in generating content, exploring new ideas, and enhancing productivity. Future developments may involve systems that collaborate with humans in creative endeavors, pushing the boundaries of innovation and expression.
- Ethical and Responsible Development: As technologies become more pervasive, the importance of ethical considerations, transparency, and accountability in development and deployment will continue to grow. Future efforts may focus on establishing ethical guidelines, regulatory frameworks, and governance mechanisms to ensure that benefits society while minimizing potential risks and harms.
- Augmented Intelligence: The future of it may involve greater integration with human capabilities, augmenting human intelligence, creativity, and decision-making processes. it technologies may empower individuals and organizations to achieve new levels of productivity, innovation, and problem-solving across diverse domains.
- Social Good: it has the potential to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges, including poverty, inequality, climate change, healthcare disparities, and education access. Future initiatives may focus on leveraging for social good, driving positive impact, and fostering equitable and sustainable development.

Pros & Cons :
it offers numerous benefits and opportunities, but it also presents challenges and potential drawbacks. Here are some of the key pros and cons:
Pros:
- Automation: it enables the automation of repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative endeavors. This leads to increased productivity, efficiency, and cost savings for businesses and organizations.
- Decision Support: it’s algorithms can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make data-driven recommendations to support decision-making processes in various domains, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and logistics.
- Predictive Analytics: it enables predictive modeling and forecasting, allowing businesses to anticipate trends, customer behaviors, and market dynamics. This helps organizations make proactive decisions and seize opportunities ahead of competitors.
- Personalization: powered recommendation systems can deliver personalized content, products, and services tailored to individual preferences and behaviors. This enhances user satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty in areas such as e-commerce, streaming platforms, and social media.
- Improved Efficiency: systems can optimize resource allocation, streamline workflows, and optimize supply chains, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost reductions for businesses and industries.
- Innovation and Creativity: technologies, such as generative models and creative tools, can assist artists, designers, writers, and musicians in generating new ideas, exploring possibilities, and pushing the boundaries of innovation and expression.
Cons:
- Job Displacement: Automation driven by it’s technologies may lead to job displacement and changes in the labor market, particularly for tasks that are routine or repetitive. This can result in unemployment, underemployment, and socioeconomic disparities if adequate measures are not taken to address the impact on workers.
- Bias and Fairness: algorithms may exhibit bias or discrimination based on the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or inequitable outcomes, particularly in areas such as hiring, lending, and criminal justice. Addressing bias and ensuring algorithmic fairness is a significant challenge in development.
- Privacy Concerns: applications often rely on vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy infringement, data breaches, and surveillance. Safeguarding sensitive information and protecting user privacy is essential to building trust and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
- Ethical Dilemmas: technologies raise ethical questions and dilemmas regarding autonomy, accountability, transparency, and the potential for unintended consequences. Ethical considerations surrounding development and deployment require careful attention to prevent harm and promote societal well-being.
- Dependency and Reliability: Reliance on systems for critical decision-making processes may create dependency and trust issues, particularly if the systems are not transparent, explainable, or reliable. Ensuring the robustness and reliability of systems is essential to prevent catastrophic failures and mitigate risks.
- Security Vulnerabilities: systems are susceptible to security threats, including adversarial attacks, data poisoning, and model stealing, which can compromise their integrity, confidentiality, and availability. Protecting systems against cyber threats and ensuring data security is crucial for safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities.
Conclusion:
it is not merely a technological advancement; it represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with machines, process information, and address complex problems. As continues to evolve and integrate into every facet of society, it is crucial to approach its development and deployment with careful consideration of ethical, societal, and economic implications.
By understanding the fundamental principles of it, exploring its diverse applications, and embracing ethical guidelines, we can harness its potential to create a more equitable, sustainable, and innovative future. As stewards of technology, we have a responsibility to ensure that it serves humanity’s best interests and fosters inclusive progress for all.
As you navigate the ever-expanding landscape of artificial intelligence, remember that curiosity, collaboration, and ethical consciousness are your greatest assets. Let us embark on this journey together, forging a path towards a future where enriches lives, empowers individuals, and catalyzes positive change on a global scale.