Best Way to Understand 5g development
Table of Contents
In the realm of telecommunications, the arrival of 5G development represents a transformative leap forward, promising unprecedented speed, connectivity, and innovation. As the successor to 4G LTE, 5G development aims to revolutionize not just how we connect, but also how industries operate and how societies function. This blog explores the intricacies of 5G development, its applications, future outlook, innovations, and benefits.
What is 5G Development?
5G Development, short for fifth-generation wireless technology, encompasses the latest iteration of mobile network standards. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is designed to offer significantly faster data speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity across a wide range of devices, from smartphones to Internet of Things (IoT) devices and autonomous vehicles. At its core, 5G leverages advanced technologies such as millimeter-wave frequencies, massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), and network slicing to achieve these improvements.
- Definition and Basics of 5G: Explain what 5G technology is, its key features (speed, latency, capacity), and how it differs from previous generations (4G, LTE).
- Technical Standards and Evolution: Discuss the standards bodies involved (e.g., ITU, 3GPP), and how 5G has evolved from concept to commercial deployment.
Why is 5G development Used?
The primary motivations behind deploying 5G are manifold:
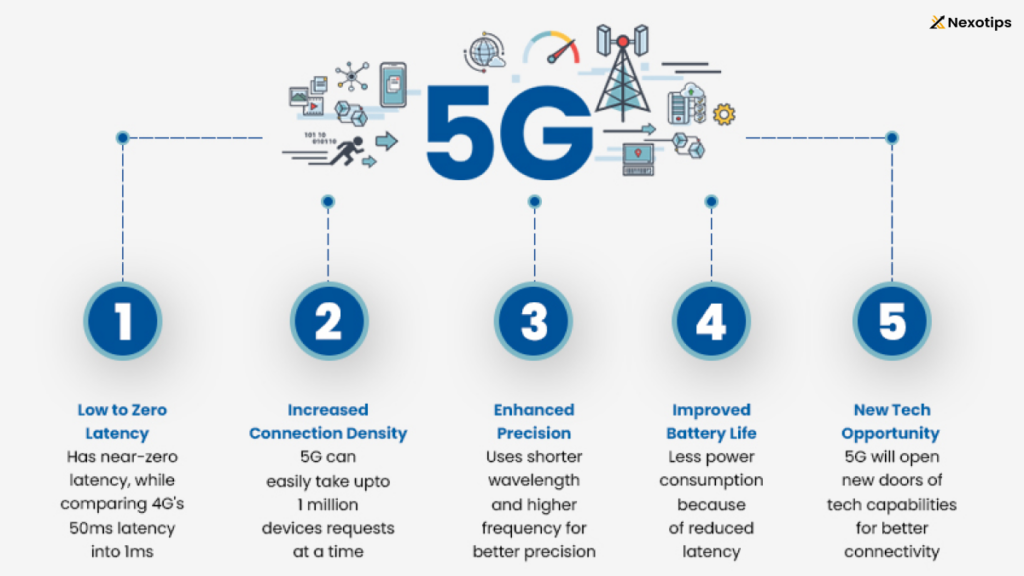
- Enhanced Speed and Capacity: 5G promises peak speeds up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps), enabling quicker downloads and seamless streaming experiences even in densely populated areas.
- Lower Latency: With latency reductions to as low as 1 millisecond (ms), 5G facilitates real-time interactions critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries.
- Support for IoT: The proliferation of IoT devices requires networks capable of handling vast numbers of connected devices simultaneously, which 5G networks can efficiently manage.
- Economic Growth: By enabling new technologies and services, 5G development is expected to spur economic growth through enhanced productivity and new business opportunities.
Current Global Deployment of 5G
- Leading Countries and Regions: Highlight which countries are at the forefront of 5G deployment (e.g., USA, South Korea, China, European nations) and their strategies.
- Infrastructure and Rollout Challenges: Discuss the challenges in deploying 5G infrastructure, including spectrum allocation, regulatory hurdles, and cost implications.
Applications and Use Cases of 5G
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Explain how 5G enhances mobile internet speeds and bandwidth, enabling applications like high-definition video streaming and augmented reality.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Explore how 5G supports a massive number of IoT devices, facilitating smart cities, connected vehicles, and industrial automation.
- Mission-Critical Services: Discuss applications in healthcare (telemedicine), public safety (smart surveillance), and remote operations (e.g., drones).
Industries Poised to Benefit from 5G
- Telecommunications: Impact on telecom operators, new revenue streams, and business models.
- Manufacturing: Role of 5G in Industry 4.0, smart factories, and predictive maintenance.
- Transportation: Applications in autonomous vehicles, traffic management, and logistics.
- Media and Entertainment: Evolution of content delivery, virtual reality (VR), and interactive experiences.
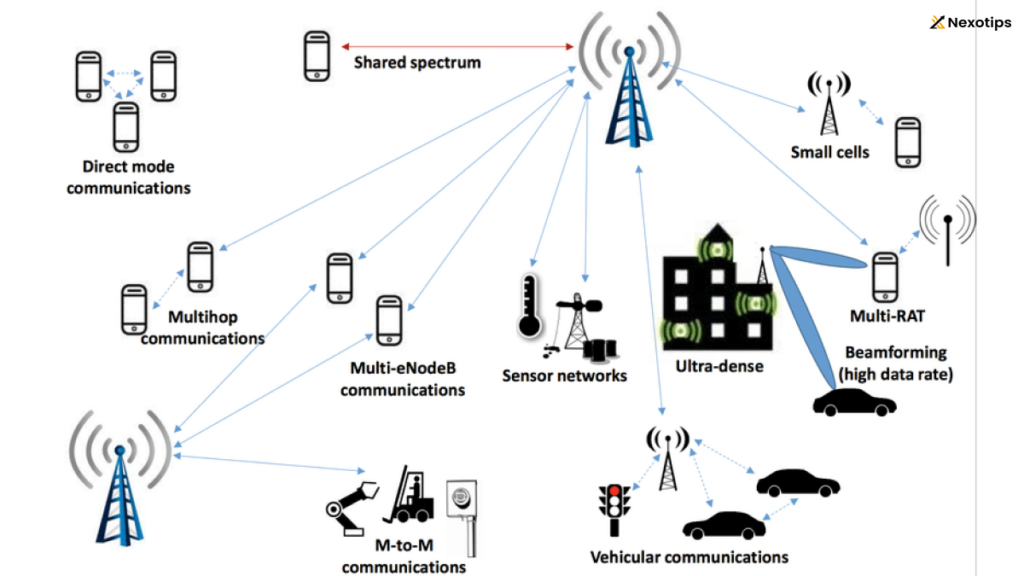
Challenges and Considerations
- Infrastructure Limitations: Address the need for dense small cell networks, fiber backhaul, and the urban-rural digital divide.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Discuss potential vulnerabilities in 5G networks and measures to mitigate risks.
- Regulatory and Spectrum Issues: Impact of spectrum auctions, international regulations, and geopolitical considerations.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of 5G development is brimming with possibilities:
- Smart Cities: 5G will enable smart city initiatives by supporting interconnected infrastructure such as traffic management systems, environmental sensors, and public safety networks.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring and telemedicine will become more effective and widespread, leveraging 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency to deliver superior healthcare services.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The automotive industry stands to benefit significantly from 5G, facilitating vehicle-to-vehicle communication and enabling autonomous driving functionalities.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: 5G’s capabilities will unlock immersive experiences in gaming, entertainment, and education through enhanced VR and AR applications.
- Industry 4.0: Manufacturing and industrial sectors will adopt 5G development to implement smart factories with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and robotic automation.
Benefits of 5g Development
- Faster Speeds: 5G networks can provide significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to 4G, potentially reaching up to 10 Gbps. This allows for quicker downloads/uploads and better streaming quality.
- Lower Latency: One of the key advancements of 5G development is its reduced latency, which means a decrease in the time it takes for devices to communicate with each other over the network. This is crucial for real-time applications like gaming, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery.
- Improved Capacity: 5G networks can support a much larger number of devices simultaneously compared to 4G. This is essential as more and more devices become connected through the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Enhanced Connectivity: Rural areas and places with limited access to traditional wired infrastructure can benefit from 5G’s ability to provide high-speed internet access wirelessly, bridging the digital divide.
- Support for IoT and Smart Devices: 5G networks are designed to handle the massive increase in connected devices expected with the growth of IoT applications, enabling smarter cities, homes, and industries.
- Innovative Applications: The high speed and low latency of 5G open up opportunities for innovative applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), remote robotic surgery, and advanced industrial automation.
- Economic Growth: 5G development is expected to drive economic growth through new business models, industries, and job creation, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on connectivity and data.
- Energy Efficiency: While 5G networks are capable of handling more data, they are also designed to be more energy-efficient compared to previous generations, which can lead to reduced overall energy consumption in network operations.
These benefits make 5G technology not only a significant upgrade over previous generations of wireless networks but also a catalyst for transformative changes across various sectors of the economy and society.
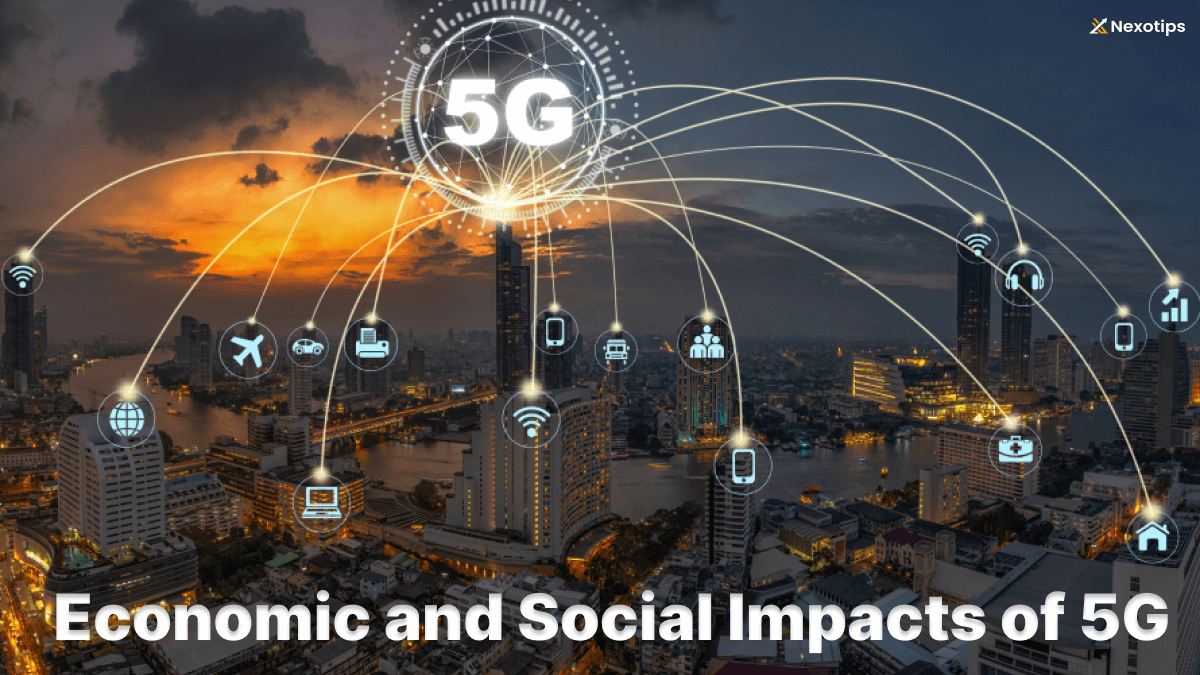
Economic Impacts :
- Growth in GDP: 5G is projected to contribute to economic growth by enabling new industries and business models. It’s estimated that 5G could add billions to global GDP over the next decade through increased productivity and new revenue streams.
- Job Creation: The rollout of 5G networks will create jobs in network deployment, maintenance, and in industries leveraging 5G capabilities such as IoT, AI, and autonomous vehicles.
- Industry Transformation: Sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and entertainment will experience transformative changes, leading to efficiency gains and new market opportunities.
- Infrastructure Investment: Deployment of 5G requires significant infrastructure investment, stimulating economic activity in construction, telecommunications equipment manufacturing, and related industries.
Social Impacts :
- Improved Connectivity: 5G promises faster and more reliable internet connectivity, reducing latency and enabling real-time applications. This will enhance user experiences and enable new services in healthcare, education, and entertainment.
- Digital Inclusion: 5G could bridge the digital divide by bringing high-speed internet to remote and underserved areas, improving access to online education, telemedicine, and government services.
- Smart Cities: 5G will support the development of smart city initiatives, with connected infrastructure for transportation, energy management, public safety, and environmental monitoring.
- Healthcare Advancements: Enhanced connectivity and data speeds could revolutionize healthcare delivery through telemedicine, remote surgery, and real-time patient monitoring.
- Environmental Impact: While 5G infrastructure may require more energy initially, it has the potential to enable more efficient resource management and reduce carbon emissions through smart grids and transportation systems.
Also Read : Unleash The Full Potential Of C++ With Object-Oriented Programming