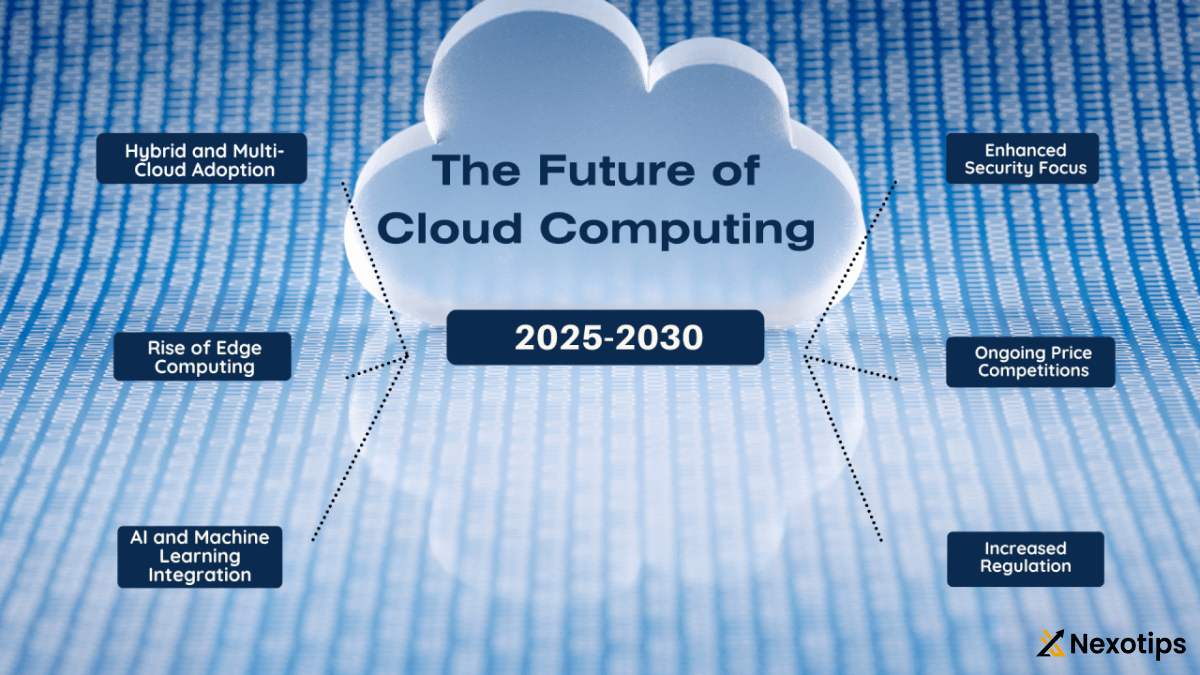
Cloud Computing Security Considerations For Enterprise Organizations In 2025
As we step into 2025, cloud computing continues to revolutionize the way businesses operate, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. However, with the increasing adoption of cloud services, security concerns have become more pronounced for enterprise organizations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the evolving landscape of cloud computing security and provide essential considerations for enterprise organizations to safeguard their data and assets in the cloud computing.
Contents :
1: The Evolving Threat Landscape in cloud computing
1.1 Rise of Cyber Threats:
- Cyber threats have evolved from simple attacks to sophisticated, multi-vector campaigns orchestrated by well-funded cybercriminal organizations and nation-state actors. Techniques such as ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), supply chain attacks, and fileless malware pose significant challenges to enterprise security.
- Enterprises must adopt a proactive approach to threat intelligence, leveraging threat hunting and incident response capabilities to detect and mitigate advanced threats before they cause significant damage.
1.2 Regulatory Compliance:
- Regulatory compliance is a complex and ever-changing landscape, with new regulations introduced regularly to address emerging security and privacy concerns. Organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions must navigate a patchwork of regulations, each with its own set of requirements and enforcement mechanisms.
- Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA requires organizations to implement robust data protection measures, conduct regular risk assessments, and demonstrate accountability and transparency in their data processing activities.

1.3 Supply Chain Risks:
- Supply chain attacks have emerged as a significant threat to enterprise security, targeting vulnerabilities in third-party vendors and service providers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Attackers exploit trust relationships and supply chain dependencies to infiltrate target organizations, often with devastating consequences.
- Enterprises must implement rigorous supply chain risk management practices, including vendor risk assessments, security due diligence, and contractual obligations for security controls and incident response.
1.4 Emerging Technologies:
- Emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, and edge cloud computing offer transformative opportunities for business innovation but also introduce new security challenges and attack surfaces. The proliferation of connected devices, AI-driven decision-making, and decentralized computing architectures necessitates a rethinking of traditional security paradigms.
- Enterprises must adopt a holistic approach to security, integrating security-by-design principles into the development and deployment of emerging technologies. This includes robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, data encryption, secure communication protocols, and continuous monitoring for anomalous behavior.
2: Key Security Considerations for Enterprise Organizations
2.1 Data Encryption and Privacy:
- Encryption is a fundamental security control for protecting data both in transit and at rest. Organizations should implement strong encryption algorithms and key management practices to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access and disclosure.
- Data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA require organizations to implement measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data, including data encryption, pseudonymization, and access controls.
2.2 Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- IAM is critical for enforcing access controls and mitigating the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. Organizations should implement IAM solutions that support granular access controls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and identity federation to ensure secure authentication and authorization.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) enables organizations to assign permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities, reducing the risk of privilege escalation and unauthorized access.
2.3 Threat Detection and Response:
- Threat detection and response capabilities are essential for identifying and mitigating cloud computing security incidents in real-time. Organizations should deploy security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to detect and respond to security threats proactively.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms enable organizations to streamline incident response processes, automate repetitive tasks, and coordinate cross-functional collaboration during security incidents.
2.4 Cloud Configuration Management:
- cloud computing configuration management is critical for reducing the risk of misconfigurations and vulnerabilities that could expose organizations to security breaches. Organizations should implement configuration management tools and practices to enforce standardized configurations, monitor changes, and remediate deviations from security baselines.
- Infrastructure as code (IaC) enables organizations to automate the provisioning and configuration of cloud computing resources, ensuring consistency, repeatability, and security across cloud computing environments.
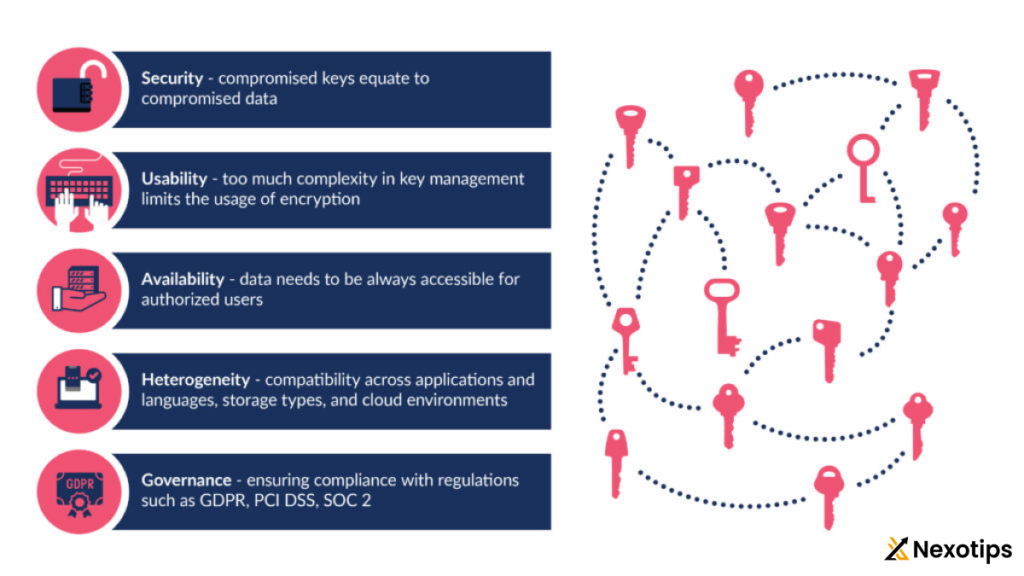
2.5 Cloud Workload Protection:
- cloud computing workload protection platforms (CWPP) are designed to protect cloud workloads from malware, exploits, and other security threats. Organizations should implement CWPP solutions that provide runtime protection, container security, and serverless security controls to safeguard cloud workloads across diverse environments.
- Continuous security monitoring and threat intelligence integration enable organizations to detect and respond to emerging threats in real-time, minimizing the risk of data breaches and service disruptions.
2.6 Secure DevOps Practices:
- Secure DevOps practices integrate security into the software development lifecycle, enabling organizations to deliver secure and resilient applications at speed and scale. DevSecOps emphasizes collaboration, automation, and continuous feedback between development, security, and operations teams to address security vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Secure coding practices, code scanning tools, and vulnerability management processes help identify and remediate security vulnerabilities in application code, libraries, and dependencies.
2.7 Third-Party Risk Management:
- Third-party risk management is essential for mitigating the risk of supply chain attacks and ensuring the security of vendor and service provider relationships. Organizations should conduct thorough due diligence and risk assessments when engaging third-party vendors, suppliers, and service providers.
- Contractual agreements should include provisions for security controls, data protection obligations, incident response procedures, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Regular monitoring and oversight of third-party performance and compliance help ensure adherence to security standards and contractual obligations.
2.8 Cloud Governance and Compliance:
- cloud computing governance and compliance frameworks provide organizations with the visibility, control, and assurance needed to maintain security and compliance across cloud environments. cloud computing security posture management (CSPM) solutions enable organizations to assess security risks, enforce compliance policies, and remediate violations proactively.
- Continuous auditing, monitoring, and reporting help organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties and reputational damage.
3: Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
3.1 Zero Trust Architecture:
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework based on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring continuous authentication and authorization for every access attempt. ZTA aims to prevent lateral movement and privilege escalation by segmenting network traffic, enforcing strict access controls, and monitoring user and device behavior.
- ZTA solutions provide organizations with granular visibility and control over network traffic, applications, and data, reducing the risk of insider threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
3.2 Quantum-Safe Cryptography:
- Quantum-safe cryptography (also known as post-quantum cryptography) is a cryptographic approach designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers. Quantum computers have the potential to break traditional cryptographic algorithms such as RSA and ECC, posing a significant risk to the security of sensitive data and communications.
- Quantum-safe cryptographic algorithms, such as lattice-based cryptography, hash-based cryptography, and code-based cryptography, offer robust protection against quantum attacks, ensuring the long-term security of cryptographic systems.
3.3 Secure Access Service Edge (SASE):
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is an emerging security architecture that converges network security and edge computing capabilities into a unified cloud-based platform. SASE integrates functions such as secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), and secure SD-WAN into a single platform, providing comprehensive security and networking services for distributed cloud computing environments.
- SASE solutions enable organizations to secure remote users, branch offices, and cloud workloads with consistent security policies and enforcement across the enterprise
Conclusion:
In 2025, the landscape of cloud computing security is characterized by evolving threats, stringent regulatory requirements, and emerging technologies. Enterprise organizations must prioritize security by implementing robust encryption, IAM, threat detection, and cloud governance practices. By staying abreast of future trends and embracing innovative security solutions, organizations can navigate the complexities of cloud computing securely and protect their valuable data and assets in the digital age.