
Exploring NFC Technology: The Power of Connectivity in the Palm of Your Hand(2024).
In an increasingly digital world, connectivity is key. From smartphones to smart homes, the ability to seamlessly interact with devices and share information has become an integral part of our daily lives. One technology that’s playing a significant role in facilitating this connectivity revolution is Near Field Communication (NFC). In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of NFC technology, exploring its capabilities, applications, and the transformative impact it’s having across various industries.
What is NFC?
NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables devices to establish communication by touching them together or bringing them into close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where two NFC-enabled devices generate radio waves to communicate when they are brought close together.

- Communication Range: NFC operates over short distances, typically up to 4 centimeters (1.5 inches). This close proximity requirement ensures secure communication between devices and prevents unauthorized access.
- Modes of Operation: NFC devices can operate in three modes: reader/writer mode, peer-to-peer mode, and card emulation mode. In reader/writer mode, an NFC-enabled device can read information from NFC tags embedded in objects like posters, labels, or smart cards. In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data, such as sharing files or contact information. In card emulation mode, an NFC-enabled device can act as a smart card, allowing it to be used for tasks like mobile payments or access control.
- Compatibility: NFC technology is widely supported across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, wearable devices, and even some laptops. Many modern smartphones come equipped with NFC capabilities, enabling users to perform a wide range of tasks, from making contactless payments to transferring files.
- Security: NFC incorporates security features to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of transmitted data. Encryption and authentication mechanisms are employed to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information. Additionally, the short-range nature of NFC communication reduces the risk of eavesdropping or interception.
- Applications: NFC technology has numerous applications across different industries. Some common uses include mobile payments (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay), transit ticketing, access control systems, data exchange between devices, and interactive marketing (e.g., NFC-enabled advertisements or posters). NFC tags are also used in product authentication, inventory management, and asset tracking.
- Limitations: While NFC offers many benefits, it also has some limitations. The short communication range restricts its use to close-proximity interactions, which may not be suitable for all scenarios. Additionally, NFC-enabled devices must be compatible and have NFC functionality enabled to communicate effectively.
Overall, NFC technology provides a convenient and secure way for devices to interact and exchange data wirelessly over short distances, making it a versatile solution for various applications in the digital world.
How Does NFC Work?
NFC (Near Field Communication) works on the principle of electromagnetic induction to enable communication between two devices when they are brought into close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. Here’s a detailed explanation of how NFC technology works:
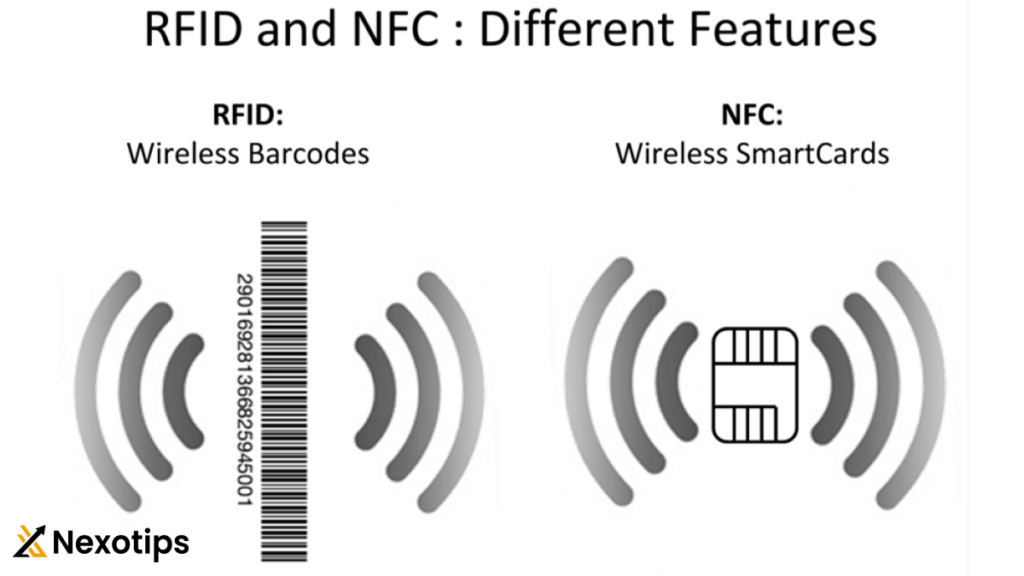
- RFID Basis: NFC technology is based on Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, which uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data wirelessly between two objects. However, NFC is an evolution of RFID that allows for two-way communication between devices, whereas traditional RFID is typically one-way communication.
- Components: NFC communication involves two main components: the NFC reader/writer device and the NFC tag or another NFC-enabled device. The NFC reader/writer device could be a smartphone, tablet, or any other device equipped with NFC functionality. The NFC tag is a passive device that contains information and is typically embedded in objects such as smart posters, labels, or cards.
- NFC devices have the capability to function in three primary modes, namely reader/writer mode, peer-to-peer mode, and card emulation mode.
- Reader/Writer Mode: In this mode, an NFC-enabled device acts as a reader or writer and can read information from NFC tags embedded in objects. For example, a smartphone with NFC functionality can read data from NFC tags on smart posters to display information or initiate actions.
- This mode enables tasks such as sharing files, photos, or contact information between two smartphones.
- Card Emulation Mode: In card emulation mode, an NFC-enabled device behaves like an NFC smart card, allowing it to be used for tasks such as mobile payments, access control, or ticketing. The device emulates the functionality of an NFC card, enabling it to interact with NFC readers as if it were an actual card.
- Data Transfer: When two NFC-enabled devices come into close proximity (typically within a few centimeters), they generate radio frequency fields. These fields enable communication between the devices and allow them to exchange data. The data transfer occurs through modulation of the electromagnetic field between the devices.
- Security: NFC incorporates security features to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of transmitted data. Encryption and authentication mechanisms are employed to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information. Additionally, the short-range nature of NFC communication reduces the risk of eavesdropping or interception.
- Applications: NFC technology has a wide range of applications, including mobile payments, transit ticketing, access control systems, data exchange between devices, interactive marketing, product authentication, inventory management, and asset tracking.
Overall, NFC technology provides a convenient and secure way for devices to communicate and exchange data wirelessly over short distances, enabling various applications in the digital world.
Applications of NFC Technology
NFC (Near Field Communication) technology has a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to its convenience, security, and versatility. Here’s a comprehensive overview of some of the most common applications:
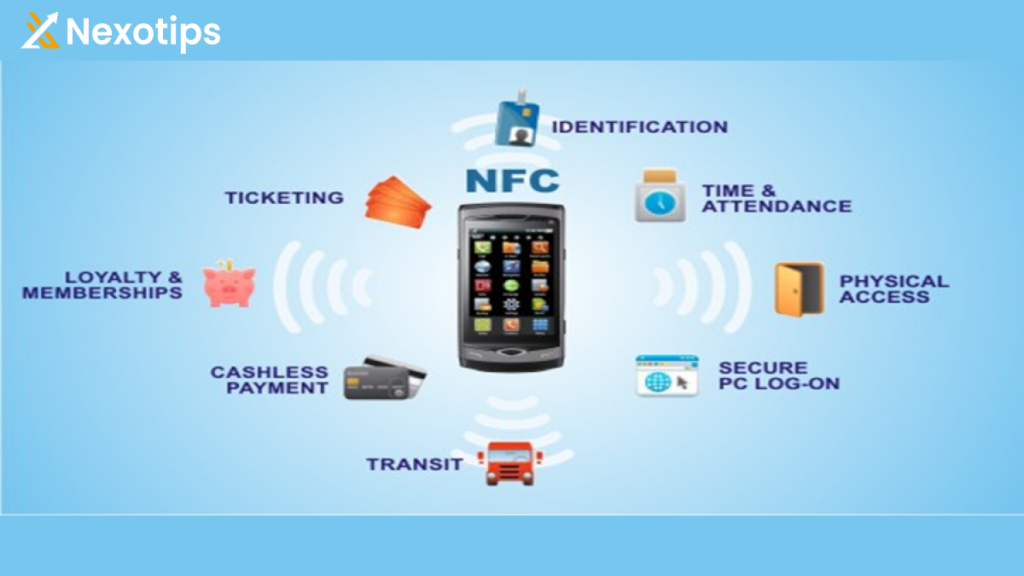
- Mobile Payments: One of the most popular applications of NFC technology is mobile payments. NFC-enabled smartphones can be used to make contactless payments at NFC-equipped point-of-sale terminals. Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay leverage NFC technology to securely transmit payment information between the smartphone and the payment terminal, enabling quick and convenient transactions.
- Transit Ticketing: NFC technology is widely used in public transportation systems for ticketing and fare collection. Commuters can use NFC-enabled smart cards or smartphones to tap and pay for bus, train, subway, or tram fares. This simplifies the ticketing process, reduces waiting times, and enhances the overall transit experience for passengers.
- Access Control and Security: NFC technology is employed in access control systems for secure entry to buildings, offices, parking garages, and other restricted areas. Employees or authorized personnel can use NFC-enabled ID cards or smartphones to authenticate their identity and gain access to secure facilities. NFC-based access control systems offer improved security, flexibility, and ease of use compared to traditional key-based or swipe card systems.
- Data Exchange: NFC enables seamless data exchange between devices, making it convenient for users to share files, photos, contact information, and other data. By simply tapping two NFC-enabled devices together, users can initiate the transfer of information without the need for cables, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth connections. This feature is particularly useful for transferring files between smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other compatible devices.
- Interactive Marketing: NFC technology is utilized in interactive marketing campaigns to engage consumers and deliver personalized experiences. Smart posters, advertisements, and promotional materials embedded with NFC tags allow consumers to access additional content, special offers, product information, or discounts by tapping their NFC-enabled smartphones on the designated area. This interactive approach enhances customer engagement, promotes brand awareness, and drives sales.
- Product Authentication: NFC tags can be embedded in products or packaging to provide authentication and anti-counterfeiting measures. Consumers can use NFC-enabled smartphones to verify the authenticity of a product by scanning the NFC tag or label. This helps to protect brands and consumers from counterfeit products and ensures product integrity throughout the supply chain.
- Inventory Management and Asset Tracking: NFC technology is employed in inventory management and asset tracking systems to streamline operations and improve efficiency. NFC tags or labels attached to items, equipment, or inventory can be scanned using NFC-enabled devices to track their movement, location, and status in real-time. This enables businesses to manage inventory, monitor assets, and optimize logistics processes more effectively.
Overall, NFC technology offers a wide range of applications across industries, enabling secure, convenient, and efficient communication, transactions, and interactions between devices, products, and people. Its versatility and ease of use make it a valuable tool for businesses, consumers, and organizations seeking to leverage the benefits of wireless connectivity and smart technology.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Security and privacy considerations are paramount when deploying NFC (Near Field Communication) technology due to the potential risks associated with wireless data transmission. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key security and privacy considerations related to NFC:
1. Data Encryption: To ensure the confidentiality of transmitted data, NFC devices should employ encryption techniques to secure the communication channel. Encryption algorithms such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) are commonly used to encrypt sensitive information exchanged between NFC-enabled devices, preventing unauthorized access or interception by malicious actors.
2. Authentication Mechanisms: NFC protocols incorporate authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of communicating devices and prevent unauthorized access. Mutual authentication between NFC devices helps establish trust and ensures that data is exchanged only between authenticated and authorized parties. Authentication protocols such as Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) and Secure Element (SE) authentication are commonly used to authenticate NFC devices securely.
3. Secure Element (SE) Integration: NFC-enabled devices may include a secure element, a tamper-resistant hardware component that stores sensitive information such as payment credentials, authentication keys, and cryptographic algorithms. Integrating a secure element in NFC-enabled devices enhances security by protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or tampering, thereby safeguarding user privacy and preventing fraudulent activities.
4. Tokenization: In the context of mobile payments and financial transactions, tokenization is a security measure used to replace sensitive payment card information with a unique identifier or token. NFC-based mobile payment systems utilize tokenization to generate a unique token for each transaction, which is transmitted securely between the NFC-enabled device and the payment terminal. Tokenization helps mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to payment card data and enhances the security of mobile payment transactions.
5. Secure Application Development: Developers should follow secure coding practices and guidelines when designing NFC-enabled applications to minimize security vulnerabilities and mitigate potential risks. This includes implementing input validation, secure data storage, encryption, and access control mechanisms to protect against common security threats such as data leakage, tampering, and unauthorized access.
6. Privacy Protection: NFC technology raises concerns about user privacy, particularly regarding the collection, storage, and sharing of personal information. To address privacy concerns, NFC-enabled applications should adhere to privacy regulations and guidelines, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, by obtaining user consent, providing transparent data practices, and implementing privacy-enhancing features such as data anonymization and pseudonymization.
7. User Awareness and Education: Users should be educated about the security and privacy implications of NFC technology to make informed decisions and adopt best practices for secure usage. This includes raising awareness about potential risks such as eavesdropping, data interception, and unauthorized access, as well as providing guidance on how to protect sensitive information and mitigate security threats when using NFC-enabled devices and applications.
Overall, addressing security and privacy considerations is essential to ensure the safe and secure deployment of NFC technology, protect user data and privacy rights, and foster trust in the reliability and integrity of NFC-enabled applications and services. By implementing robust security measures, adhering to privacy principles, and promoting user awareness and education, organizations can mitigate risks and build confidence in the use of NFC technology for various applications and use cases.
The Future of NFC Technology
The future of NFC (Near Field Communication) technology is promising, with ongoing advancements and innovations driving its evolution and expanding its potential applications. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the potential trends and developments shaping the future of NFC:
- Enhanced Security Features: As NFC technology continues to be adopted for a wide range of applications, there will be a growing emphasis on enhancing security features to protect against emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This may include the integration of advanced encryption algorithms, biometric authentication, and secure element technologies to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data.
- Widespread Adoption in IoT: NFC technology is well-suited for integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling seamless connectivity and communication between IoT devices, sensors, and systems. In the future, NFC-enabled IoT solutions are expected to proliferate across various industries, facilitating smart home automation, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, and environmental monitoring, among other applications.
- Contactless Payments and Digital Wallets: The adoption of contactless payments and digital wallets is expected to continue growing, driven by consumer demand for convenient, secure, and frictionless payment experiences. NFC-enabled smartphones and wearables will play a central role in enabling contactless payments, transit ticketing, loyalty programs, and mobile commerce, leading to further displacement of traditional payment methods.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: NFC technology will be increasingly integrated with emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and wearable devices to create immersive and interactive user experiences. For example, NFC-enabled AR applications could enable users to interact with physical objects and digital content seamlessly by tapping their NFC-enabled devices on designated areas.
- Expansion of NFC-based Services: The versatility of NFC technology will drive the expansion of NFC-based services beyond traditional applications such as mobile payments and transit ticketing. Future applications may include NFC-enabled healthcare solutions for patient monitoring and medical device connectivity, NFC-based authentication and access control systems for smart buildings and smart cities, and NFC-enabled retail experiences for personalized marketing and customer engagement.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Efforts to promote interoperability and standardization of NFC technology will be crucial for fostering its widespread adoption and ensuring compatibility between NFC-enabled devices, platforms, and ecosystems. Standardization bodies and industry consortia will continue to develop and refine NFC standards and protocols to facilitate seamless interoperability and interoperable solutions across different domains and applications.
- Advancements in NFC Chip Technology: Continued advancements in NFC chip technology, including improvements in power efficiency, data transfer speed, and form factor miniaturization, will drive the development of smaller, more energy-efficient NFC chips for integration into a wide range of devices and form factors. This will enable the proliferation of NFC-enabled devices in diverse applications, from consumer electronics to wearable devices to industrial IoT solutions.
Overall, the future of NFC technology is characterized by its versatility, convenience, and security, making it a key enabler for the next generation of connected devices, smart services, and digital experiences. As NFC technology continues to evolve and mature, it will play an increasingly integral role in shaping the future of commerce, communication, and connectivity in our interconnected world.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Near Field Communication (NFC) technology stands as a beacon of connectivity in our increasingly digital world. Its ability to facilitate seamless data exchange between devices in close proximity has ushered in a new era of convenience, efficiency, and innovation across a myriad of industries. From enabling contactless payments and access control to fostering smart marketing strategies and IoT connectivity, NFC has woven itself into the fabric of our daily lives, enriching our experiences and redefining the way we interact with technology.
However, as with any technology, it’s crucial to remain mindful of security and privacy considerations. By implementing robust encryption, authentication protocols, and user awareness, we can harness the full potential of NFC technology while safeguarding against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Looking ahead, the future of NFC technology is brimming with possibilities. With ongoing advancements driving improvements in chip design, antenna technology, and security measures, we can expect NFC-enabled devices to become even more versatile, secure, and ubiquitous. As NFC continues to evolve and expand its reach, it will undoubtedly play an instrumental role in shaping the future of connectivity, ushering in a world where seamless interactions are not just a possibility, but a reality.
Must watch: NFC Forum
Others: 5 Transformative Ways Voice Recognition Super Charges Mobile Apps
One thought on “Exploring NFC Technology: The Power of Connectivity in the Palm of Your Hand(2024).”